What is Sharding in Blockchain? Let’s find out
Contents
Exchange crypto at best rates
Proceed to exchange
To witness significant and noticeable amounts of growth, there is a compulsion for that particular website or application to scale. This is to ensure that the flow of traffic on the platform does not lower down its effectiveness and speed. Especially in connection with the blockchain and cryptocurrency. While blockchains are being rolled out at a very fast pace, what it truly lacks is scalability. Why? Because almost all of it is dependent on pilot programs; be it financial transactions or supply chain management. Scalability has been seen as a major issue in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Sharding, in particular, is being majorly explored by developers and is one of the many methods that are aimed at increasing the transactional throughput. Here a few questions are expected to be asked: what exactly is sharding, what is the history of it, how does it work, and many more, all of which will be answered in the following article.
What is sharding?
It is a database architectural pattern that is related to horizontal partitioning. In horizontal partitioning, separation is done from one table’s rows to several tables which then become known as partitions. These partitions have the same schemas and columns but rows that are entirely different from one another. Consequently, the data that is present in each partition is unique in its own way and is not dependent on the data that is stored in other partitions.
Apart from horizontal partitioning, vertical partitioning is also present. What happens in this type of partitioning is that the columns are separated as a whole and are then put into distinct tables afterward. Like horizontal partitioning, the data in vertical partitioning is also unique with it containing distinct columns and rows. The data in each vertical partition is also independent of the data in other partitions.
When did it appear?
The main problem while storing data on a database is that every database has the compulsion to live on one server. Upon hitting the maximum capacity of the server, you can do absolutely nothing to prevent the situation that you are stuck in. Thus, sharding came as a breakthrough to serve this very purpose. For instance, when on 3rd April 2012 Instagram was launched, more than 1 million downloads were done within the first 24 hours. From a business point of view, that sounds remarkable but for the engineers, this is a massive headache. It was through the process of sharding that they were able to add 1 million new users in 24 hours. Over the course of the last decade, sharding has become a popularized concept, mainly because of its relevance with blockchain technology and the crypto world.
What is sharding in blockchain?
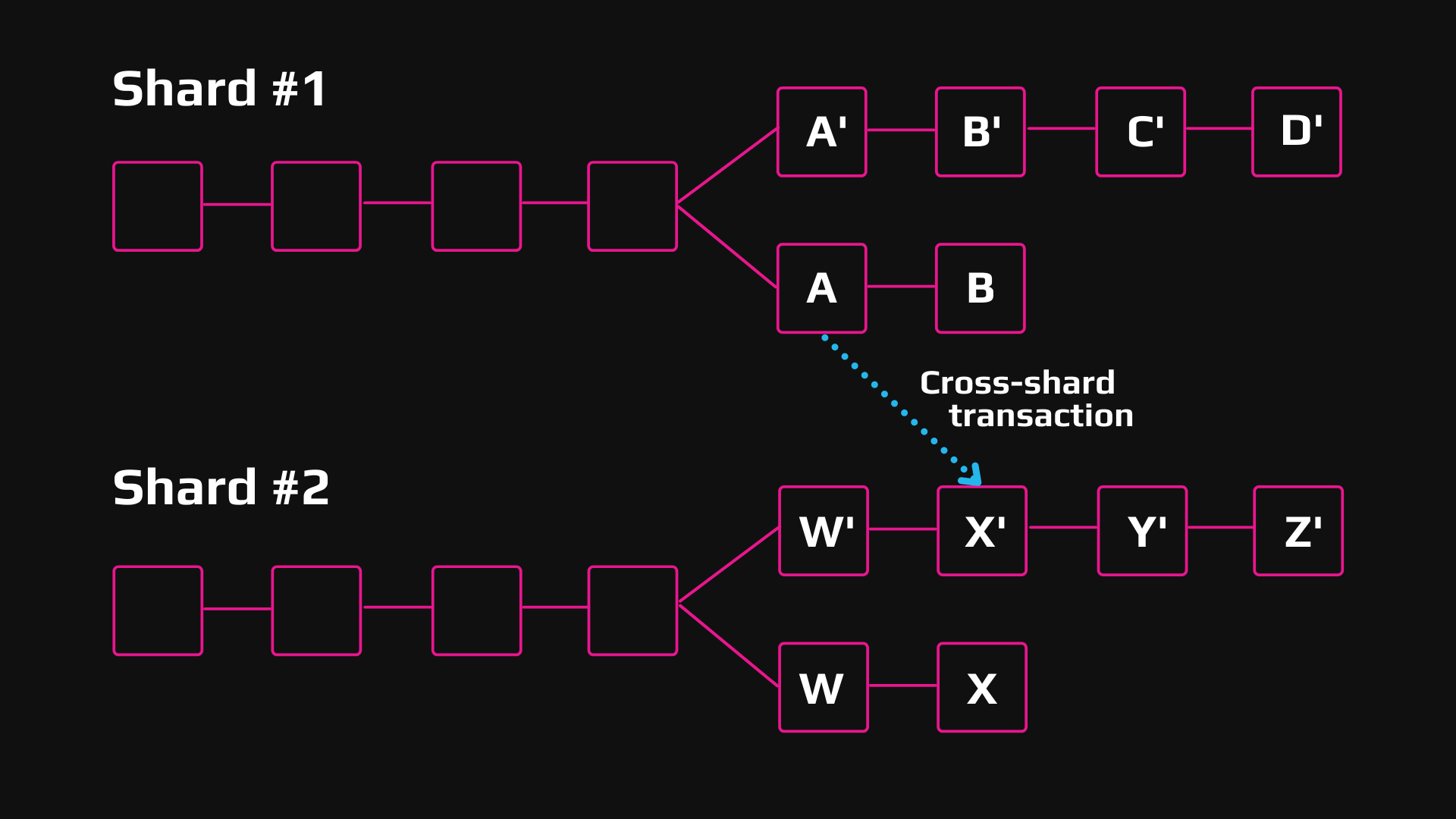
In recent times, blockchain protocols and cryptocurrencies have managed to gain great momentum due to which there is a huge user influx. Because of this, more transactions are being made which tends to slow down the system. For this very purpose, blockchain sharding steps in.
To explain sharding simply, it would be correct to say that it is a way of partitioning with the purpose to make the database more efficient. The computational and workload across peer-to-peer, also known as the P2P network, is spread out to ensure that each node is not held responsible for the processing of the whole network’s transactional load. Instead of this what is done is that every node is responsible for the maintenance of the information concerning its partition or shard. The information that the shard contains can still be accessible to other nodes making the ledger not only decentralized but also secure.
How does it work?
Having discussed horizontal and vertical partitioning, there are certainly more details attached to the process of sharding. Sharding includes the breakdown of data into smaller pieces which are known as “logical shards”. Followed up is the distribution of these logical shards across different database nodes called physical shards. The specialty of these physical shards is that they can store several logical shards.
What is utterly interesting is the fact that the database operates on a “shared-nothing architecture”. As the name suggests, the shards are kept in all their anonymity as none of the data or the computing resources are shared amongst them. However, in some cases, tables might be replicated in each shard as the reference tables.
What problems does sharding solve?
Among the major reasons prompting the use of sharding is how it manages to speed up the entire process of query response and everything that comes with it. Upon submitting a query on the database that is not sharded, there is a possibility that it may have to go through every single row in the table that one is querying for before it is in the position to find the result set that they are looking for. This can slow down queries. Through sharding, the queries have to go through a lesser number of rows which in return fastens the process of query response.
Apart from that, sharding also helps in increasing the reliability of the application. This is done by reducing the effect that the outages may have caused. For instance, if your application is fully reliant on a database that is not sharded, then an outage can always make the entire application unavailable. This can be in the form of cyber-attacks and breaches because it is highly likely for the attacker to attack only one single shard. Sharding helps in reducing the overall effect.
What cons does it have?
First off, it increases the overall complexity of applying a database that is shared. This makes it risky. In a case, if someone implements a shared database incorrectly, then that would cause the blockchain to be exposed to cyber-attacks. Also, after the separation of records into different databases, it is not convenient at all to go back to the original unsharded database architecture. What this does is that it harms the backup of transactional records and as a result, the data is put at risk.
Apart from that, another drawback is that there is a limit to separating databases into distinct shards in vertical sharding. This depends on the power of the server and powerful servers tend to be extremely expensive.
Cryptocurrencies that are using sharding
Among the cryptocurrencies that are using sharding are:
- Ethereum
- NEAR
- Polkadot
Many of these coins have not only made a name for themselves, but they have also experienced success in terms of their value and worth. Thus, the success of these cryptocurrencies shows the influential role played by sharding in the field of blockchain and crypto.
Conclusion
Sharding is an extremely important development for cryptocurrencies as it helps in decentralization and keeping the platforms secure. However, it does come with a lot of complexities attached to it which may be considered as a drawback by many. What must be kept in mind is the consumer’s need according to which he should invest in sharding and the entire procedure of setting up a sharded database.